Rice is more than just a staple food. For billions of people around the world, it is a way of life, a tradition, and a reflection of cultural identity. Among the many varieties of rice cultivated across Asia and beyond, Banskathi Rice holds a distinctive place. Known for its unique fragrance, texture, and nutritional richness, it is a variety that resonates with both tradition and modern culinary practices.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore Banskathi Rice in detail, including its origins, cultivation methods, nutritional value, cultural importance, health benefits, economic role, and culinary uses. We will also compare it with other rice varieties, examine its role in local economies, and discuss future opportunities for farmers and consumers.
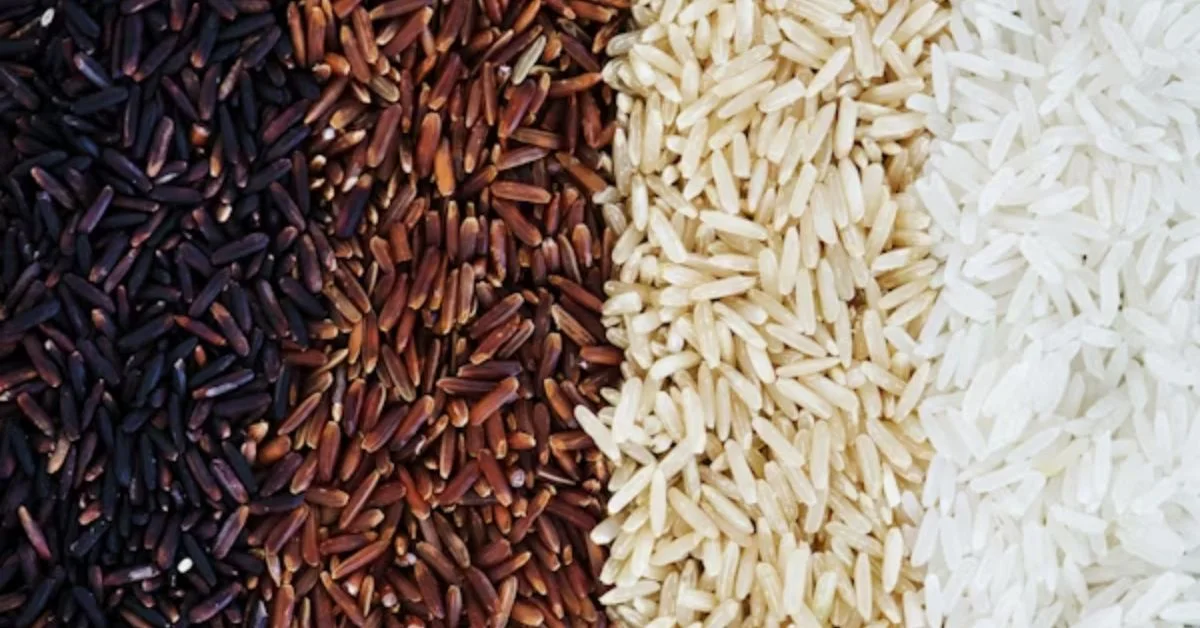
What is Banskathi Rice?
Banskathi Rice is a medium-to-long grain aromatic rice variety traditionally cultivated in parts of India and Bangladesh. It has a delicate fragrance, somewhat similar to basmati but less intense, and a soft, non-sticky texture when cooked. Its appeal lies in its versatility: it can be used for daily meals, festive dishes, and even health-conscious diets.
The name “Banskathi” itself is associated with regional dialects, often linked to local agricultural heritage. Unlike mass-commercialized rice, Banskathi retains a traditional touch and reflects the agricultural wisdom of communities that have cultivated it for generations.
Origins and History of Banskathi Rice
The history of Banskathi Rice can be traced back centuries in Eastern India and parts of Bangladesh. Farmers in these regions experimented with hybrid forms of rice to produce a grain that was not only aromatic but also adaptive to local soil and climatic conditions.
Unlike high-profile export varieties such as Basmati, Banskathi Rice was initially grown for local consumption. Families preserved its seeds and passed them through generations, ensuring that the variety retained its unique qualities.
Over time, demand grew due to its taste, affordability, and cooking flexibility. This made Banskathi an important player in local rice markets, often bridging the gap between everyday household needs and festive culinary demands.
Cultivation of Banskathi Rice
Banskathi Rice thrives in alluvial soils and semi-humid climates, making Eastern India’s fertile river basins ideal for its cultivation.
Key Cultivation Stages
- Seed Selection: Farmers carefully preserve seeds from previous harvests, ensuring purity of variety.
- Land Preparation: Fields are ploughed and leveled to allow water retention, as rice is highly water-dependent.
- Transplantation: Seeds are sown in nurseries and later transplanted into the main field after 20–25 days.
- Irrigation Management: Continuous water supply is maintained, but careful drainage prevents fungal diseases.
- Fertilization: Organic manure, along with minimal chemical inputs, is often preferred to maintain soil health.
- Harvesting: After around 135–150 days, rice stalks turn golden yellow and are harvested manually or mechanically.
Table: Ideal Growing Conditions for Banskathi Rice
| Factor | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Climate | Semi-humid, tropical to subtropical |
| Soil Type | Alluvial, loamy, nutrient-rich |
| Water Requirement | 1200–1500 mm during growth cycle |
| Growth Duration | 135–150 days |
| Temperature Range | 20–35°C |
This cultivation process not only ensures good yield but also retains the nutritional and aromatic properties of Banskathi Rice.
Nutritional Value of Banskathi Rice
Banskathi Rice is not just about aroma; it is also nutrient-dense. While polished rice loses some nutritional content, semi-polished or parboiled Banskathi retains much of its goodness.
Table: Nutritional Composition of Banskathi Rice (per 100g uncooked)
| Nutrient | Approximate Value |
|---|---|
| Energy | 340–360 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | 75–78 g |
| Protein | 7–9 g |
| Fat | 0.5–1.5 g |
| Fiber | 1.5–2 g |
| Calcium | 10–12 mg |
| Iron | 1–2 mg |
| Magnesium | 20–25 mg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.1–0.2 mg |
This nutritional profile makes Banskathi Rice a healthy energy source suitable for all age groups.
Health Benefits of Banskathi Rice
Banskathi Rice offers multiple health benefits due to its balanced nutritional content:
- Provides Sustained Energy – Its high carbohydrate content makes it a great energy source for daily activities.
- Good for Digestion – The soft texture and moderate fiber content make it easy to digest.
- Low in Fat – Ideal for weight management when consumed in controlled portions.
- Rich in Micronutrients – Contains small but essential amounts of iron, magnesium, and B vitamins.
- Gluten-Free – Naturally safe for people with gluten intolerance.
- Supports Satiety – When paired with vegetables or protein, it keeps hunger at bay.
Culinary Uses of Banskathi Rice
Banskathi Rice is prized in the kitchen for its flavor, aroma, and versatility. Unlike sticky rice varieties, it remains fluffy after cooking, making it suitable for diverse recipes.
Common Culinary Applications
- Daily Meals: Served with curries, lentils, or vegetables.
- Festive Dishes: Used in pulao, biryani, or kheer (sweet rice pudding).
- Regional Specialties: Often included in local recipes where aroma plays a key role.
- Modern Fusion: Integrated into global dishes such as rice salads or fried rice.
Table: Culinary Comparison of Banskathi Rice
| Dish Type | Why Banskathi Fits Well |
|---|---|
| Plain Steamed Rice | Fluffy, aromatic, complements any curry |
| Biryani/Pulao | Absorbs spices without turning sticky |
| Desserts (Kheer) | Mild aroma enhances sweetness |
| Fried Rice | Retains shape and texture |
| Rice Salads | Light, non-sticky, easy to mix with veggies |
Banskathi Rice vs. Other Popular Rice Varieties
| Feature | Banskathi Rice | Basmati Rice | Sona Masoori Rice | Gobindobhog Rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain Size | Medium to long | Long and slender | Medium | Short |
| Aroma | Mild fragrance | Strong fragrance | Mild | Distinct, sweet |
| Texture | Soft, fluffy | Long, separate grains | Light, fluffy | Sticky when cooked |
| Cooking Use | Everyday + festive | Festive, special | Daily consumption | Traditional dishes |
| Cost | Affordable | Premium, higher cost | Moderate | Moderate |
This comparison shows how Banskathi strikes a balance between affordability, taste, and versatility.
Economic Importance of Banskathi Rice
Rice is central to the agricultural economy of South Asia, and Banskathi plays a role at the local and regional levels.
- For Farmers: Provides steady income due to consistent demand.
- For Traders: Creates market opportunities in both retail and wholesale.
- For Consumers: Offers a balance of affordability and quality.
Export opportunities are emerging too, as consumers abroad search for aromatic but affordable alternatives to basmati.
Cultural and Traditional Importance
In many regions, Banskathi Rice is linked to festivals, rituals, and traditional feasts. It is often chosen for special occasions because of its fragrance and ability to pair well with rich gravies. In rural households, serving guests Banskathi rice dishes is considered a gesture of warmth and respect.
Challenges in Banskathi Rice Cultivation
Despite its strengths, farmers face challenges in cultivating Banskathi Rice:
- Water Dependence: Requires significant irrigation.
- Pest/Disease Vulnerability: Susceptible to fungal infections if drainage is poor.
- Market Competition: Competes with premium varieties like Basmati.
- Price Fluctuations: Farmers sometimes struggle with unstable market rates.
Solutions include organic farming, better irrigation practices, and government support through fair pricing schemes.
Future of Banskathi Rice
With rising consumer interest in healthy and aromatic food, Banskathi Rice has significant future potential:
- Organic Banskathi Rice: Growing demand in health-conscious markets.
- Export Markets: Affordable alternative to high-priced premium rice.
- Branding & Packaging: Farmers’ cooperatives can brand Banskathi as a regional specialty.
- Agro-Technology: Improved irrigation and pest control can enhance yields.
Conclusion
Banskathi Rice is more than just food—it is a story of culture, tradition, and resilience. With its rich aroma, nutritional benefits, versatility in cooking, and economic significance, it holds a special place in both households and markets. While it may not carry the global fame of Basmati, Banskathi is treasured for its balance of quality and affordability.
Its future lies in sustainable cultivation, branding, and awareness, ensuring that this rice variety continues to thrive in both traditional kitchens and modern dining tables around the world.
FAQs
1. What is Banskathi- Rice known for?
It is known for its mild fragrance, fluffy texture, and versatile use in both everyday meals and festive dishes.
2. Is Banskathi Rice healthy?
Yes, it provides energy, moderate protein, low fat, and essential micronutrients while being easy to digest.
3. How is Banskathi- Rice different from Basmati?
Basmati is more aromatic and slender-grained, while Banskathi is mildly fragrant, softer, and more affordable.
4. Can Banskathi- Rice be used for biryani?
Yes, it absorbs spices well and remains fluffy, making it a good choice for pulao and biryani.
5. Where is Banskathi- Rice mainly grown?
It is traditionally cultivated in Eastern India and parts of Bangladesh, especially in fertile river basin soils.
For more information, click here.