Sammying- Leather is one of the oldest and most versatile materials known to humanity. From primitive times when hides were dried and softened by hand to modern industries producing high-quality fashion, upholstery, and technical leathers, the journey of leather-making has always relied on carefully designed steps. Among these steps, samying plays a vital yet often underappreciated role.
Samying is the process of mechanically removing water from hides or skins after tanning and before drying. This stage ensures that the leather has the right moisture content for further mechanical operations like splitting, shaving, and stretching. Without samying, hides would remain too wet, leading to inefficiencies, inconsistent thickness, and a higher risk of bacterial damage.
In this article, we will explore samying in great detail—its purpose, historical evolution, machines used, process mechanics, advantages, challenges, and future innovations. We will also compare it with other leather processing stages, examine its significance in modern sustainable tanneries, and explain why it remains one of the cornerstones of quality leather production.
Understanding the Role of Sammying in Leather Making
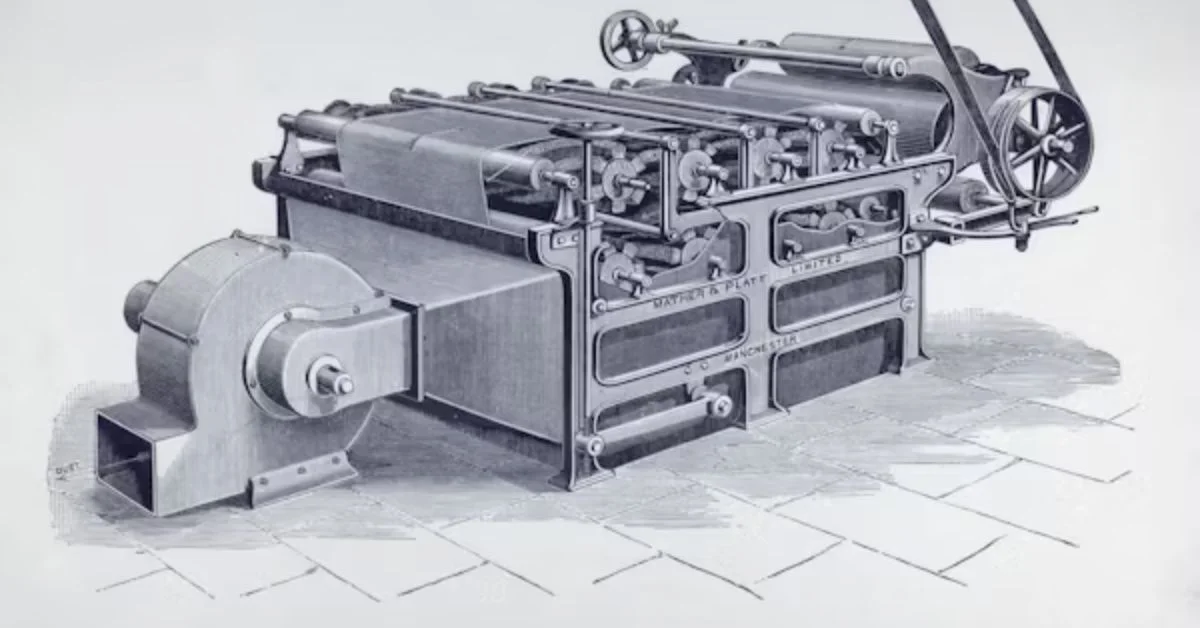
The term “samying” comes from the specialized samying machine, a large piece of industrial equipment designed to squeeze water out of hides through rollers. After tanning, hides contain 65–80% water, which makes them heavy and difficult to handle. If sent to the next stage in this condition, they could:
- Stretch unevenly under mechanical forces.
- Develop bacterial growth due to high moisture.
- Slow down production because of the added weight.
- Lead to inconsistencies in final leather thickness and softness.
Samying reduces this water content to about 45–55%, striking a balance between flexibility for further operations and stability to prevent microbial damage.
Thus, the importance of samying lies not only in efficiency but also in ensuring quality, uniformity, and durability of the final leather.
Historical Development of Sammying
Before mechanization, hides were dried by hand squeezing, wringing, or pressing between absorbent materials. These methods were time-consuming, labor-intensive, and inconsistent.
The first dedicated samying machines appeared during the industrial revolution in the 19th century, when mechanized rollers were introduced into tanneries. These early machines applied pressure to hides, expelling water in a more uniform way than manual labor could achieve.
By the 20th century, hydraulic and pneumatic samying machines became common, improving efficiency further. Today, modern samying machines feature precision rollers, vacuum assistance, and automated controls that reduce energy consumption and improve yield.
The Mechanics of Sammying
To appreciate how sammying works, one must understand its mechanical process.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Loading the Hide:
The wet tanned hides are placed onto the feed section of the sammying machine. - Roller Compression:
Large rollers exert pressure, squeezing water from the hide fibers. The pressure is carefully regulated to avoid damaging the grain surface. - Water Extraction:
The water squeezed out drains away, collected for treatment or recycling. - Moisture Balancing:
By the end of the process, the hide retains enough water to remain flexible for further operations.
Table: Moisture Reduction by Samying
| Stage of Processing | Approximate Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Post-tanning (before) | 65–80% |
| Post-samying (after) | 45–55% |
This controlled reduction is crucial. Too little water removed makes hides unwieldy, while too much can cause them to dry prematurely and stiffen.
Types of Sammying Machines
Samying machines have evolved to suit different tannery needs. Below are the most common types:
| Machine Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Single-roller | Uses one large roller to compress hides. Compact but less efficient. | Small-scale operations. |
| Double-roller | Two rollers provide higher efficiency and uniform water extraction. | Medium to large tanneries. |
| Vacuum-assisted | Combines roller pressure with suction, improving drying speed. | High-volume production. |
| Automated samying | Features programmable pressure settings and sensors for precision. | Modern sustainable tanneries requiring control. |
Advantages of Sammying
Sammying may seem like just a step in leather making, but its benefits ripple throughout the entire process.
- Improved Workability: Reduced water content makes hides easier to split, shave, and stretch.
- Consistency: Uniform moisture ensures even thickness and smoother finishing.
- Reduced Energy Use: Pre-drying hides through sammying lowers the load on later drying systems.
- Hygienic Protection: Lower moisture reduces the chance of bacterial or fungal growth.
- Enhanced Final Quality: Good sammying translates into softer, more durable, and evenly finished leather.
Challenges in Sammying
Despite its advantages, sammying also comes with challenges that require careful management:
- Risk of Grain Damage: Excessive pressure can leave roller marks or damage the grain.
- Operator Skill: Incorrect settings may lead to under- or over-squeezing.
- Maintenance Costs: Modern machines require regular servicing to maintain precision.
- Environmental Concerns: Wastewater collected must be treated to prevent pollution.
Thus, skilled operation and sustainable practices are critical in ensuring sammying delivers benefits without drawbacks.
Sammying vs. Other Leather Processing Steps
Sammying often gets compared to other stages like setting out or drying. While related, they serve different purposes.
| Process | Purpose | When Performed |
|---|---|---|
| Sammying | Removes excess water by roller compression. | After tanning, before splitting/shaving. |
| Setting Out | Smooths, stretches, and flattens the hide. | After sammying. |
| Drying | Removes most of the remaining water. | Later finishing stages. |
This distinction shows how sammying is a preparatory step ensuring other processes work effectively.
Innovations in Modern Sammying
As sustainability becomes central to leather production, sammying technology is evolving:
- Energy-efficient motors reduce power consumption.
- Water recycling systems capture and reuse water extracted from hides.
- Smart automation adjusts roller pressure based on hide thickness.
- Eco-friendly lubricants in machines reduce environmental impact.
- Integration with digital monitoring systems allows real-time performance analysis.
These innovations help tanneries remain competitive in a global market where both quality and environmental responsibility matter.
Table: Future Directions in Sammying
| Innovation | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| AI-driven automation | Greater precision, reduced operator error. |
| Sustainable water systems | Minimized waste and pollution. |
| Lightweight machine design | Lower energy requirements. |
| Hybrid drying integration | Faster processing with less equipment. |
Conclusion
Sammying may not be the most glamorous step in leather processing, but it is unquestionably one of the most important. By removing just the right amount of water, sammying prepares hides for the complex transformations that follow. Without it, the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of leather production would suffer greatly.
From its historical roots in manual pressing to its modern evolution with vacuum-assisted and automated systems, samying reflects the broader story of leather making itself: a balance between tradition, innovation, and precision. As industries embrace eco-friendly practices and digital tools, samying will continue to adapt, ensuring that the world’s demand for high-quality leather is met responsibly.
FAQs
Q1: What is samying in leather processing?
Samying is the process of mechanically reducing water content in hides after tanning, preparing them for further processing.
Q2: Why is samying important?
It ensures hides remain workable, prevents bacterial growth, reduces energy needed for drying, and improves overall leather quality.
Q3: How much moisture does samying remove?
Typically, it lowers water content from 65–80% to around 45–55%, leaving hides flexible but stable.
Q4: What machines are used for samying?
Common machines include single-roller, double-roller, vacuum-assisted, and fully automated samying machines.
Q5: How is modern samying becoming more sustainable?
Through innovations like water recycling, energy-efficient motors, smart automation, and eco-friendly lubricants.
For more information, click here.