Among the many innovations in construction, one of the most reliable and cost-effective methods has been the pole barn system. Central to this method is the pole barn pole, the structural element that defines strength, stability, and function. These poles act as the backbone of the building, supporting roofs, walls, and overall design.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore every aspect of pole barn poles: their history, construction methods, types of materials, installation techniques, applications in agriculture and industry, advantages and disadvantages, durability, maintenance practices, and their evolving role in modern construction.
The Origins of Pole Barn Construction
Pole barns as a concept began in the early 20th century when farmers and builders sought affordable ways to create large, open storage buildings. Instead of traditional foundations, which were costly and time-consuming, they used long wooden poles set deep into the ground. These poles supported beams and trusses, creating sturdy structures without complex masonry.
This innovation led to the widespread adoption of pole barns across agricultural communities. Today, the design remains popular because it is simple, economical, and highly adaptable.
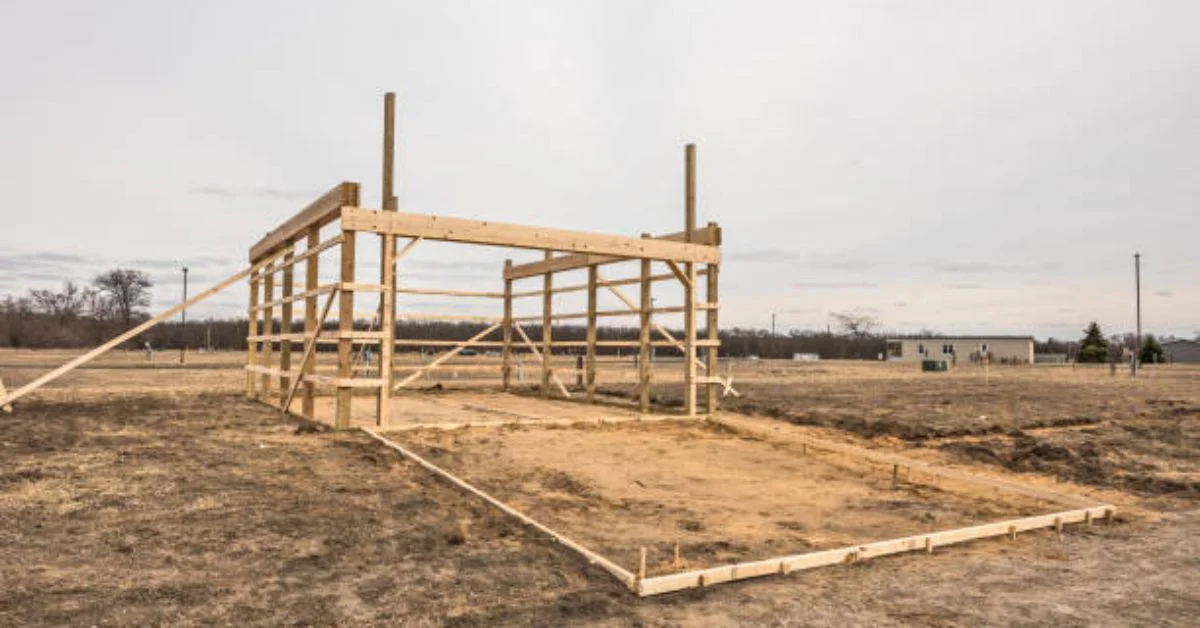
What Is a Pole Barn Pole?
The pole barn pole is the primary vertical support member of a pole barn structure. Unlike conventional framed buildings that rely on concrete foundations, pole barns rely on poles embedded in the ground to carry loads.
Functions of a Pole Barn Pole:
- Structural Support: Bears the weight of the roof and side walls.
- Foundation Replacement: Serves as both frame and foundation when buried securely.
- Wind Resistance: Anchors the structure against strong winds.
- Flexibility: Allows for wide, open interior spaces without many interior walls.
Types of Pole Barn Poles
Different pole materials serve different purposes. Choosing the right type depends on the intended use of the barn, budget, and environmental conditions.
Table: Types of Pole Barn Poles
| Type | Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wooden Poles | Pressure-treated lumber | Affordable, easy to source, traditional. | Prone to rot, insects, shorter lifespan. |
| Steel Poles | Galvanized or coated steel | Extremely durable, resistant to pests. | Higher cost, requires special tools. |
| Concrete Poles | Reinforced concrete | Very strong, long-lasting, rot-proof. | Heavy, hard to install, costly. |
| Hybrid Poles | Wood with steel reinforcement | Balance of affordability and strength. | Installation more complex. |
Selecting the Right Pole for a Pole Barn
When choosing a pole barn pole, several factors come into play:
- Load Requirements: The taller and wider the barn, the stronger the poles must be.
- Soil Conditions: Sandy soil may require deeper or broader pole bases, while clay provides more natural grip.
- Climate Factors: Areas with heavy snow loads or high winds need reinforced poles.
- Budget: While wood is cheaper, steel or concrete may provide long-term savings through durability.
Pole Barn Pole Dimensions
Poles vary in size depending on the design of the barn.
- Common Lengths: 10 to 24 feet.
- Common Thickness: 6×6 inches or larger for wooden posts; steel poles vary by gauge.
- Depth of Burial: Usually one-third of the pole length is set underground for stability.
Example:
A 16-foot barn wall might require poles that are 20 feet long, with 4 feet buried underground.
Installation of Pole Barn Poles
Proper installation ensures the barn remains strong for decades.
Step-by-Step Overview:
- Site Preparation: Clear and level the ground.
- Marking: Layout the pole positions, usually 8 to 12 feet apart.
- Digging Holes: Holes are dug with augers or post-hole diggers.
- Pole Placement: Poles are set into holes with gravel or concrete backfill.
- Alignment: Ensure poles are plumb (perfectly vertical).
- Securing: Concrete footers or compacted gravel provide additional stability.
Durability of Pole Barn Poles
The lifespan of a pole barn pole depends heavily on material and treatment.
- Wooden Poles: Typically last 15–40 years if pressure-treated. Untreated wood lasts far less.
- Steel Poles: Can last over 50 years with proper coatings.
- Concrete Poles: Often exceed 75 years with minimal maintenance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity:
- Apply protective coatings to wood.
- Avoid direct soil contact by using barriers or sleeves.
- Inspect regularly for damage or decay.
- Replace compromised poles immediately to prevent structural failure.
Applications of Pole Barn Poles
Pole barns are not limited to farming—they serve a wide variety of purposes.
Agricultural Applications
- Barns for livestock (cattle, horses, poultry).
- Storage for hay, feed, and farm equipment.
- Machine sheds for tractors and tools.
Commercial Applications
- Warehouses and workshops.
- Retail spaces in rural areas.
- Storage units.
Residential Applications
- Garages or carports.
- Hobby workshops.
- Homes designed with pole barn framing.
Recreational Applications
- Arenas for riding or sports.
- Event spaces.
- Community halls.
Benefits of Pole Barn Poles
- Cost Efficiency: Pole barns are cheaper to build than traditional buildings.
- Speed of Construction: Fewer materials and simpler design reduce build time.
- Flexibility: Poles allow for open floor plans with no interior walls.
- Durability: When properly maintained, poles provide decades of service.
- Adaptability: Structures can be extended or modified easily.
Challenges of Pole Barn Poles
- Wood Rot and Insects: A concern for wooden poles in damp or termite-prone areas.
- Upfront Costs: Steel or concrete poles are expensive initially.
- Installation Depth: Poorly installed poles can lead to structural instability.
- Environmental Concerns: Treated wood may release chemicals into soil.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular inspections and repairs are necessary.
Comparing Pole Barn Poles to Traditional Foundations
| Aspect | Pole Barn Poles | Traditional Foundations |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low to moderate. | High (concrete-intensive). |
| Construction Speed | Fast, minimal excavation required. | Slow, requires curing and heavy work. |
| Flexibility | Easy to modify or expand. | Modifications are complex. |
| Durability | Moderate to high depending on material. | High, often lasts 100+ years. |
| Skill Requirement | Moderate, DIY possible. | Requires skilled labor. |
Environmental Considerations
Pole barn poles affect the environment differently based on materials:
- Wood: Renewable but must be treated, raising chemical concerns.
- Steel: Recyclable but energy-intensive to produce.
- Concrete: Very durable but leaves a heavy carbon footprint during production.
Future Trends in Pole Barn Poles
The construction industry continues to innovate pole barn designs:
- Composite Materials: Using recycled plastics mixed with wood for poles.
- Eco-Friendly Treatments: Safer preservatives for wooden poles.
- Prefabricated Poles: Easier installation and consistent quality.
- Smart Coatings: Anti-corrosion and anti-rot technologies.
These advancements will make pole barn poles even more reliable and sustainable in the future.
Conclusion
The pole barn pole is more than just a structural element—it is the foundation of a versatile, affordable, and reliable building system. From farms to homes, from warehouses to arenas, pole barn poles support countless applications. The choice of material, installation method, and maintenance plan determines the long-term value of these poles.
As construction technology evolves, pole barn poles will continue to be adapted with eco-friendly materials, improved durability, and innovative designs that balance cost and sustainability. For farmers, business owners, and homeowners alike, the pole barn pole remains a symbol of practical ingenuity and structural strength.
FAQs
1. What is a pole barn pole made of?
Pole barn poles can be made of wood, steel, concrete, or hybrid materials, with each offering unique benefits and drawbacks.
2. How deep should pole barn poles be set?
Generally, one-third of the pole’s length should be buried underground, often between 3 to 6 feet, depending on height and soil.
3. How long do wooden pole barn poles last?
Pressure-treated wooden poles can last 15–40 years with proper maintenance, while untreated poles deteriorate much faster.
4. Can pole barn poles be replaced?
Yes, damaged poles can be replaced, but the process requires careful lifting and reinforcement of the existing structure.
5. What is the best material for pole barn poles?
The best material depends on budget and environment: wood is affordable, steel is durable, and concrete offers long-term strength.
For more information, click here.